The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development

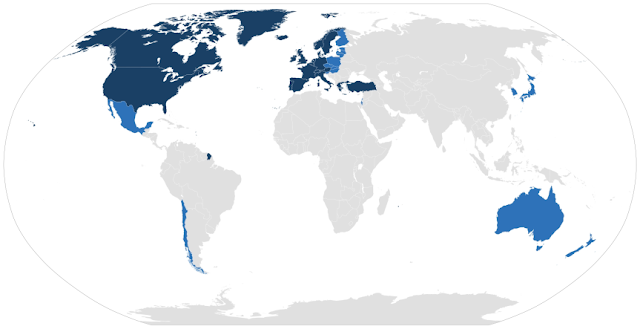
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) is an intergovernmental economic organization founded after World War II, in 1961. It has 36 member States, which, most of them, are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index. The OECD was created after European leaders realized that the best way to ensure lasting peace was to encourage co-operation and reconstruction, rather tan punish the defeated. It is for this that its main purpose is to stimulate economic progress and world trade. Its official languages are English and French and the headquarters of the organization are in Paris. This is how it looks like: The Secretary-General is José Ángel Gurría, the Deputy Secretary-General are Ludger Schuknecht and Masamichi Kono. OECD, as an international organization, is financed by its member States. Its Budget for last year was €374 million.