Member States
The OECD is a forum of countries describing themselves as commited to democracy and the market economy. We may say that it is a platform to compare policies, seeking answers to common problems, identify good practices and a way of coordinating domestic and international policies of its members.
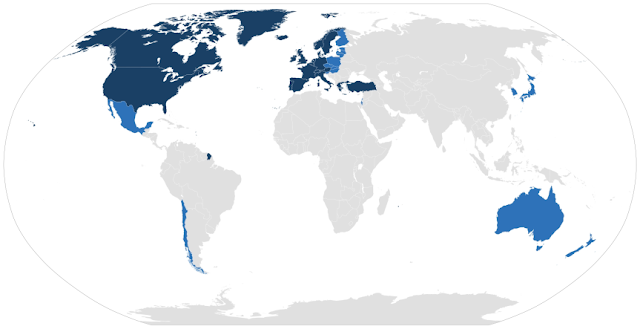
As previously mentioned, The OECD is composed of 36 member States. They are: Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Chile, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Korea, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Mexico, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovak Republic, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, United Kingdom and United States.
Here we have a chart with member States and the date on which they started to be members of the organization:
In addition to this States, European Commission representatives participate alongside Members in discussions on the OECD´s programme, and are involved in the work of the entire organization and its different bodies. However, it does not have the right to vote and does not officialy take part in the adoption of legal instruments submitted to the Council for adption.
Over time, OECD´s focus has broadened to include extensive contacts with non-Members and it now mantains co-operative relations with a large number of them.
There are also key partners: Brazil, India, People´s Republic of China, Indonesia and South Africa. Together with them, the OECD brings around its table 39 countries that account for 80% of world trade and investment, giving it a pivotal role in addressing the challenges facing the world economy.
As previously mentioned, The OECD is composed of 36 member States. They are: Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Chile, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Korea, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Mexico, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovak Republic, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, United Kingdom and United States.
Here we have a chart with member States and the date on which they started to be members of the organization:
In addition to this States, European Commission representatives participate alongside Members in discussions on the OECD´s programme, and are involved in the work of the entire organization and its different bodies. However, it does not have the right to vote and does not officialy take part in the adoption of legal instruments submitted to the Council for adption.
Over time, OECD´s focus has broadened to include extensive contacts with non-Members and it now mantains co-operative relations with a large number of them.
There are also key partners: Brazil, India, People´s Republic of China, Indonesia and South Africa. Together with them, the OECD brings around its table 39 countries that account for 80% of world trade and investment, giving it a pivotal role in addressing the challenges facing the world economy.





Comentarios
Publicar un comentario